Structural & Material Laboratories
Structural Laboratory
The following equipment is also available
- One 1000-Kip MTS Universal Testing Machine (Tension/Compression)
- Two 110-Kip MTS Universal Testing Machine (Tension/Compression)
- Four MTS 458 analog controllers with function generators to control the actuators
|
Quantity |
Load Capacity |
Stroke |
Servo-Valve |
Velocity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
35 kips |
10 in. |
15 gpm |
|
|
1 |
165 kips |
5 in. |
15 gpm |
|
|
2 |
110 kips |
10 in. |
15 gpm |
|
|
4 |
22 kips |
24 in. |
180 gpm |
100 in/sec. |
There is a unique direct shear machine in the laboratory for testing the shear behavior of rock joints, concrete crack interfaces, and masonry mortar joints. The machine can apply a maximum vertical force of 734 kN (165 kips) with a servo-controlled hydraulic actuator and a maximum horizontal shear force of 156 kN (35 kips) under cyclic shear reversals.
Controllers
Three MTS 493 controllers which can provide control to three additional actuators in our Hybrid Testing System.
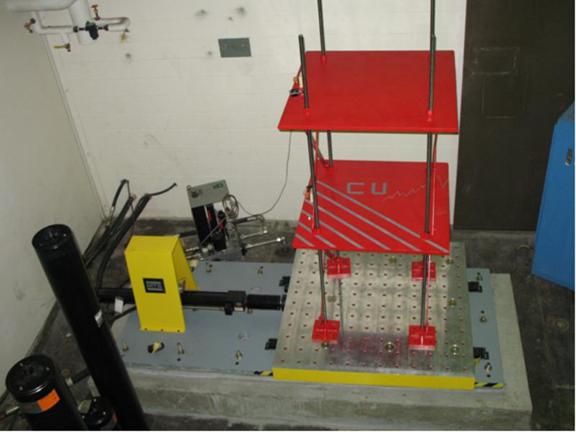
MTS Shake Table
The structural engineering and mechanics laboratory is equipped with a 1.5m x 1.5m uniaxial shaking table manufactured by MTS Systems Corp. The table is driven by a 10,000-lb actuator capable of 18 in of stroke and equipped with a 30 gpm servovalve. The table weighs 2160 lb and can support a payload of 4000 lb. The table is setup to be controlled digitally by a National Instruments PXI controller through an MTS 458 analog controller. The PXI controller can function either as a supervisory controller, or as a feedback controller by switching the servovalve input in the 458 analog controller.

Material Laboratory
The Materials Laboratory that is adjacent to the Structures Laboratory has three MTS load frames.
One of load frame has 1000-kip load capacity and is equipped with hydraulic tension grips. In addition, this machine has two additional horizontal actuators, each with a capacity 130 kips in tension and 165 kips in compression, for bi-axial testing. Each of the actuators can be controlled separately by an analog controller.
The second load frame has a load capacity of 110 kips.
The third load frame has a load capacity of 110 kips and is equipped with hydraulic tension grips and an environmental chamber. The grips have temperature regulated extension rods that are designed for use with high and low temperatures. The hydraulic piston in the load frame is controlled by a digital controller. The temperature in the environmental chamber can be controlled between -40°C and 177°C with a control accuracy of ±1°C. The humidity range is between 10% and 95% relative humidity.
Durability testing equipment for concrete and other materials
- Shrinkage testing apparatus
- Creep testing frame for concrete specimens
- Creep loading setup for adhesives
- Rapid chloride permeability testing system (ASTM C1202)
- Long-term chloride penetration - 90-day ponding test (AASHTO T259)
- Experimental system for ASTM C1260 (ASR) and ASTM C452 (sulfate attack)
- Crack resistant for drying shrinkage (the ring test)
Microscopes and Accessories
- One trinocular desktop microscope (40x-200x) with fiber optics light source
- One microscope lens (10x)
- One CCD color video camera
- One hot stage
- Two x-y micropositioning platforms
- One PC with image grabber
- One TV monitor for image monitoring
- One VCR for image recording
Environmental chambres
- Two environmental chambers (+20°C to +90°C)
- One freezing-thawing chamber
Cement Production Equipment
- One high temperature furnace (up to 1500°C)
- One jar mill
- Accessories for cement production
Others
- Experimental system for coupled environmental and mechanical loadings, including a 110-kip MTS machine coupled with a set of 110-kip hydraulic grips and an environmental chamber (temperature -30°C to 177°C and humidity 20% to 95%).
- Ultrasonic testing equipment (E-meter and V-meter)
- 3-D high precision scanner (surface roughness)
- Chemical analyses (e.g. chloride concentration)
- Penetrometer for asphalt viscosity
- Fiber optics strain sensoring system (a fiber optics data acquisition system and a PC)